How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from understanding basic drone components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from legal regulations and safety procedures to essential maintenance and troubleshooting tips, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your drone adventures.
We will explore the intricacies of drone controls, camera operation, and advanced maneuvers, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the skies. Understanding battery management and emergency procedures is crucial, and we’ll delve into these critical aspects as well. By the end of this guide, you will possess the skills and knowledge to operate your drone responsibly and creatively.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will detail the key parts of a typical drone, provide definitions for common terms, and compare different battery types.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the interplay of several key components. Each plays a vital role in enabling flight and image capture.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, move, and hover. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this onboard computer receives input from various sensors and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the transmitter.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power to the motors and other components. The battery’s capacity directly impacts flight time.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): A GPS module allows the drone to pinpoint its location, enabling features like autonomous flight, return-to-home, and geofencing.
- Camera: Captures images and videos. The quality of the camera varies greatly depending on the drone model, ranging from basic HD to high-resolution 4K and beyond.
Glossary of Common Drone Terms
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology is essential for understanding manuals, troubleshooting, and communicating with other drone enthusiasts.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a consistent altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mounting system for the camera, reducing camera shake and improving image quality.
- Payload: The weight carried by the drone, including the camera and any additional equipment.
- RTF (Ready-To-Fly): A drone that comes fully assembled and ready to fly out of the box.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees in real-time.
- Geofencing: Setting virtual boundaries for the drone’s flight area.
Comparison of Drone Battery Types
Different battery types offer various performance characteristics. The choice depends on factors like flight time requirements and budget.
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Typical Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | 3.7-14.8 | 500-5000+ | 10-30+ |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | 3.8-15.2 | 500-5000+ | 10-30+ (slightly longer than LiPo) |
| LiFe (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | 3.2-12.8 | 500-5000+ | 10-30+ (generally shorter than LiPo/LiHV) |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for responsible drone operation. This section will Artikel essential checks and guidelines.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously check the drone and its components to ensure safe operation.
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Check battery charge level and ensure proper connection.
- Verify GPS signal acquisition.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Review weather conditions and ensure safe wind speeds.
- Check surrounding airspace for any obstacles or restrictions.
Safety Guidelines for Drone Operation
Responsible drone piloting involves adhering to legal regulations and prioritizing safety.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
- Avoid flying near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace.
- Respect people’s privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly only in permitted areas and comply with all local and national regulations.
- Be aware of other aircraft and avoid collisions.
- Never operate a drone under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Safe Launch and Landing Procedure
A systematic approach to launching and landing ensures a smooth and safe flight.
Launch:
1. Power on the transmitter.
2. Power on the drone.
3.
Wait for GPS signal lock.
4. Calibrate the compass.
5. Perform pre-flight checks.
6. Slowly lift off.
Landing: 1. Initiate descent slowly. 2.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable flying experience.
Maintain a controlled descent. 3. Gently lower the drone to the ground. 4. Power off the drone.
5. Power off the transmitter.
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic drone controls is essential for safe and controlled flight. This section explains the functions of the control sticks and Artikels fundamental maneuvers.
Drone Transmitter Controls
Most drone transmitters use two joysticks to control the drone’s movement. Each stick controls a different aspect of the flight.
- Left Stick (Yaw and Throttle): Vertical movement controls altitude (up/down), while horizontal movement controls rotation (yaw – left/right).
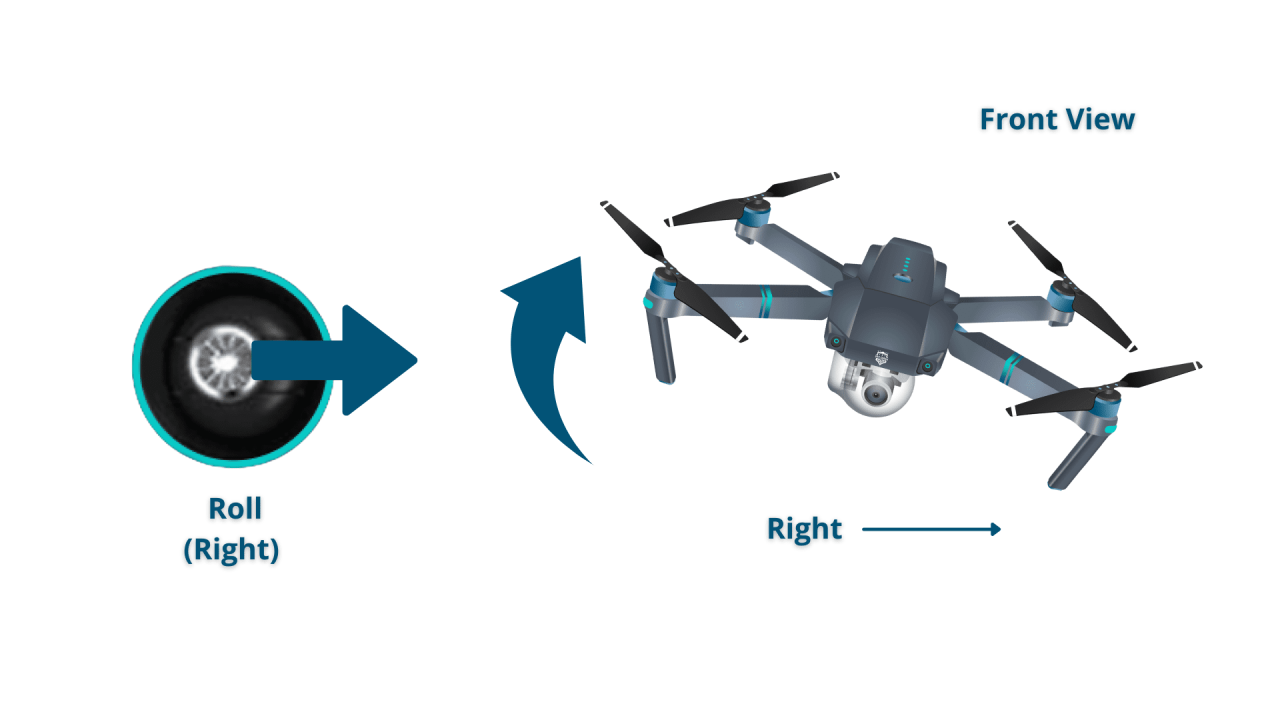
- Right Stick (Pitch and Roll): Vertical movement controls forward/backward movement (pitch), while horizontal movement controls side-to-side movement (roll).
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Mastering these fundamental maneuvers is crucial for safe and confident drone operation.
- Takeoff: Gently increase the throttle on the left stick to lift the drone vertically.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady altitude and position by carefully adjusting the throttle and sticks.
- Forward/Backward Movement: Push the right stick forward to move forward and backward to move backward.
- Sideways Movement: Push the right stick left or right to move sideways.
- Rotation (Yaw): Rotate the drone by moving the left stick left or right.
Emergency Landing Procedure, How to operate a drone
Knowing how to perform an emergency landing is crucial for mitigating potential risks.
- Reduce throttle to initiate a slow descent.
- Maintain control and avoid sudden movements.
- Gently lower the drone to the ground.
- Power off the drone and transmitter.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, pilots can explore advanced techniques to enhance their aerial capabilities and capture more creative shots.
Precise Hovering and Smooth Transitions
Precise hovering requires a delicate touch and understanding of wind conditions. Smooth transitions between flight modes, such as from GPS mode to Attitude mode, require practice and familiarity with the drone’s controls.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability.
- Attitude Mode: The drone maintains its orientation relative to the pilot’s controls, regardless of wind conditions. This mode is ideal for close-range maneuvers and precise control.
- GPS Mode: The drone uses GPS data to maintain its position and altitude, making it more stable in windy conditions. This mode is useful for longer flights and aerial photography.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): This automated function allows the drone to return to its takeoff point, useful in case of signal loss or low battery.
Flight Controller Comparison

Different flight controllers offer varying features and performance characteristics. Factors to consider include processing power, sensor integration, and firmware support.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Optimizing camera settings and understanding different shot types are key to capturing high-quality aerial footage.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture allows for optimization of image quality in various lighting conditions. Higher ISO values are suitable for low-light conditions, but can increase image noise. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds can create motion blur.
Capturing Different Shot Types
Experimenting with different shot types enhances visual storytelling.
- Aerial Panoramas: Stitching together multiple overlapping images to create a wide-angle view.
- Time-lapses: Capturing a series of images over time and compiling them into a video, showing changes over an extended period.
- Video Footage: Recording continuous video, ideal for showcasing movement and dynamic scenes.
Utilizing Camera Features
Features like zoom, focus, and image stabilization enhance image quality and creative control.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its optimal performance.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Common issues include propeller damage, battery issues, and software glitches. Regular inspections and preventative maintenance can help avoid many problems.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regular cleaning and inspection of the drone’s components are vital for preventing malfunctions and extending the drone’s lifespan. Use appropriate cleaning tools and materials to avoid damaging sensitive electronics.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A maintenance schedule helps prevent unexpected issues and ensures the drone remains in optimal condition. The frequency of maintenance will depend on usage and environmental conditions.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and complying with drone regulations is crucial for responsible and legal drone operation.
Local and National Regulations
Regulations vary by location, so it is crucial to research and understand the specific laws and rules in your area. These often include registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational guidelines.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones
Many areas are restricted for drone flight, including airports, military bases, and sensitive infrastructure. It’s essential to use drone flight planning software or apps to identify and avoid these restricted zones.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need permits or licenses to operate a drone legally. These permits often require additional training and background checks.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
Effective aerial photography and videography relies on understanding visual composition principles.
Principles of Visual Composition
Applying principles like the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry enhances the visual appeal of aerial shots. Understanding light and shadow is also crucial for capturing compelling images.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
Examples of Effective Aerial Shots
- High-angle shots: Provide a broad overview of the landscape.
- Low-angle shots: Emphasize the scale and grandeur of a subject.
- Dynamic tracking shots: Follow a moving subject, adding a sense of movement and excitement.
- Unique perspectives: Offer fresh and unusual viewpoints.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Experimenting with different camera angles and perspectives creates compelling visual narratives.
Battery Management and Charging: How To Operate A Drone
Proper battery management is crucial for safety and extending the lifespan of your drone batteries.
Safe Charging Procedures
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow all safety instructions. Never leave batteries unattended while charging and ensure proper ventilation.
Proper Storage and Handling
Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Avoid dropping or puncturing batteries, and always handle them with care.
Signs of a Damaged or Faulty Battery
Signs of a damaged battery include swelling, leaking, unusual heat generation, or inconsistent performance. Never use a damaged battery, and dispose of it properly.
Emergency Procedures and Failsafes
Understanding emergency procedures and failsafe mechanisms is crucial for mitigating risks during drone operation.
Failsafe Mechanisms

Many drones incorporate failsafe mechanisms, such as automatic return-to-home (RTH) in case of signal loss or low battery. Understanding how these mechanisms function is vital for safe operation.
Steps to Take in Case of Malfunction or Signal Loss
In case of a malfunction or signal loss, immediately initiate the RTH function if available. If not, attempt to regain control and perform a controlled emergency landing. If unable to regain control, secure the area and report the incident.
Emergency Contact Information
Keep a list of emergency contact information for drone-related incidents readily available. This may include local authorities, drone manufacturers, and relevant regulatory bodies.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding experience that opens up a world of possibilities. From breathtaking aerial photography to efficient data collection, drones offer a unique perspective and valuable tools. By diligently following the safety guidelines and best practices Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently take to the skies, capturing stunning visuals and exploring new heights.
Remember responsible operation and adherence to regulations are paramount for a safe and enjoyable experience.
Common Queries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is recommended before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced a significant change in magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If the signal is lost, the drone will automatically attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always remain vigilant and be prepared to take manual control if possible.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight time varies significantly depending on the drone model, battery capacity, and flight conditions (wind, payload). Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local civil aviation authority’s website for specific regulations regarding drone operation in your area. The FAA (in the US) and similar agencies in other countries provide comprehensive guidelines.
